What is HMI?
An HMI SCADA system is a user interface or control panel that connects a person with a machine, system or device. Although the term can technically be applied to any screen that allows the user to interact with a device, the HMI is most commonly used in the context of industrial processes that control and monitor production machines.
On the other hand, HMI is short for Human Machine Interface . Similarly, among professionals, its translation into Spanish Man-Machine Interface is often used to refer to this type of operator panel.
A common example is an ATM that we all use in everyday life. In this case, the screen and the push buttons allow the machine to dispense bills, enter money, among other operations.
Human Machine Interface (HMI) systems enable reliable technology operations in every application, including high-speed trains, CNC machining centers, semiconductor production equipment, and laboratory or diagnostic medical equipment.
In short, the HMI interface encompasses all the elements that a person will touch, see, hear, or use to perform control functions and receive feedback on those actions.
Thus, an operator or maintenance personnel can control or monitor the machinery from the HMI, it can include information such as temperature, pressure, production process steps, calculation of necessary materials, exact positions of the production lines, control of the levels of tanks with raw materials among many other functions.
Additionally, these control panels can be connected to PLCs and display their problem-solving behavior for maintenance technicians, saving valuable money.
What is an HMI for?
HMI screens are used to optimize an industrial process by digitizing and centralizing data. In this way, operators can view important information on graphs, digital dashboards, view and manage alarms, and connect to SCADA and MES systems through a console.
The human-machine interface communicates with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and input / output sensors to obtain and display information for users to see. Similarly, they can be used for a single function, such as monitoring and tracking, or for more sophisticated operations, such as shutting down machines or increasing production speeds, depending on how they are implemented.
Previously, operators had to visually review mechanical progress and record it on a sheet of paper or a whiteboard. Today, PLCs can communicate real-time information directly to an HMI screen.
Consequently, this technology eliminates the need for these manual practices and therefore reduces many costly problems caused by lack of information or human error.
As data takes on an increasingly essential role in manufacturing, the future looks bright for HMI operator panels. This technology may have come a long way, but its growth potential remains virtually unlimited.
On the other hand, a well-designed HMI system does more than just present control and information functions; provides the operator with intuitive active functions to perform on the results of those actions and information on system performance.
So another of the important concepts of its design is the usability of the control panel. In other words, its functions and handling must facilitate the life of the operator and the technicians involved in the manufacturing processes.
The Basic Functions of the HMI include:
- Visualize the Data
- Production Time Tracking
- Monitor KPIs
- Monitor the Inputs and Outputs of the Machines
- Basic Block Diagram of an HMI/Human Machine Interface
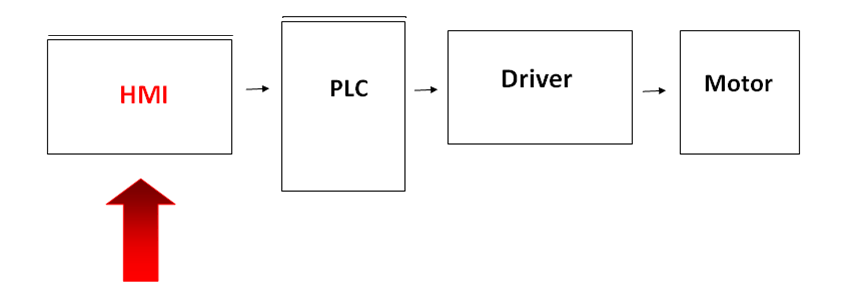
Types of HMI or Human Machine Interfaces
The Man-Machine Interface can be presented in different formats, from screens built into machines, computer monitors, to touch screens and mobile devices, but regardless of their format or the term used to refer to them, its purpose is to provide information on mechanical performance and the development of production processes.
In the last decade, changes in business and operational needs have led to exciting developments in HMI technology. Now, it is becoming more and more common to see evolved HMI models. These more modern interfaces are creating more opportunities for team interaction and analysis.
High Performance HMI
Increasingly, operators and users are moving towards a high-performance HMI, an HMI design method that helps ensure fast and efficient interaction. By drawing attention to only the most necessary or critical indicators in the interface, this design technique helps the viewer see and respond to problems more efficiently, as well as make better-informed decisions.
The high performance HMI indicators are simple, clean and free of extraneous controls or graphics. Other design elements, such as color, size, and location, are used discreetly to optimize the user experience.
Touch Screens and Mobile Devices
Touchscreens and the mobile HMI are two examples of the technological advancements that have come with the advent of smartphones. Instead of buttons and switches, modernized mobile versions allow operators to touch the physical screen to access controls.
Touch screens are especially important when used with a mobile device, which is deployed through web-based SCADA systems or through an application. The mobile HMI offers a variety of benefits to operators, including instant access to information and remote monitoring.
Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring allows greater flexibility and accessibility for both operators and managers. With this feature, an external control systems engineer can, for example, confirm a warehouse temperature on a handheld device, eliminating the need for on-site monitoring after work hours.
These days, testing a process at your production plant while it’s miles away from the facility may not seem like something out of the ordinary.
Network and Cloud HMI
Network HMIs are also in high demand because they allow operators to access data and visualization from field devices. Additionally, it is becoming increasingly common to send data from local HMIs to the cloud, where it can be accessed and analyzed remotely, while maintaining control capabilities at a local level.
Who uses the HMI screen?
HMI technology is used by almost all industrial organizations, as well as by a wide range of companies in different sectors, to interact with their machines and optimize their industrial processes.
Industries that use HMI include:
- Energy
- Food and Drinks
- Manufacturing
- Oil and Gas
- Power
- Recycling
- Transport
- Water and Sewage
Within the production staff interact with HMI operators, system integrators and engineers, especially engineers control systems. The Human Machine Interface is an essential resource for these professionals, who use it to review and monitor processes, diagnose problems and visualize data.
For their process they use specific software so that the engineers can program them correctly. This software allows the engineer to design what the operator will see on the screen, what they can monitor, what buttons can be pressed, and how the operator can manipulate the machine.
The systems engineer who designs the operator panel has to program each indicator and button to a specific input or output direction of a PLC, so they must be compatible and understand the same language or protocol. Consequently, the most common protocols in the industry are Modbus, Industrial Ethernet, and Profibus. These are responsible for connecting the PLC , HMI / SCADA , machinery and other devices of the production process.
What is the difference between HMI and SCADA?
The Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and HMI are closely related, and often referred to them in the same context, since both are part of a system for industrial control wider, but each offers different functionalities and opportunities.
While HMIs are focused on transmitting information visually to help the user monitor an industrial process , SCADA systems have a greater capacity for data collection and control system operation.
Unlike SCADA systems, HMIs do not collect or record information or connect to databases. Rather, the interface provides an effective communication tool that works as part of, or in conjunction with, a SCADA system. Learn more about HMI SCADA.



