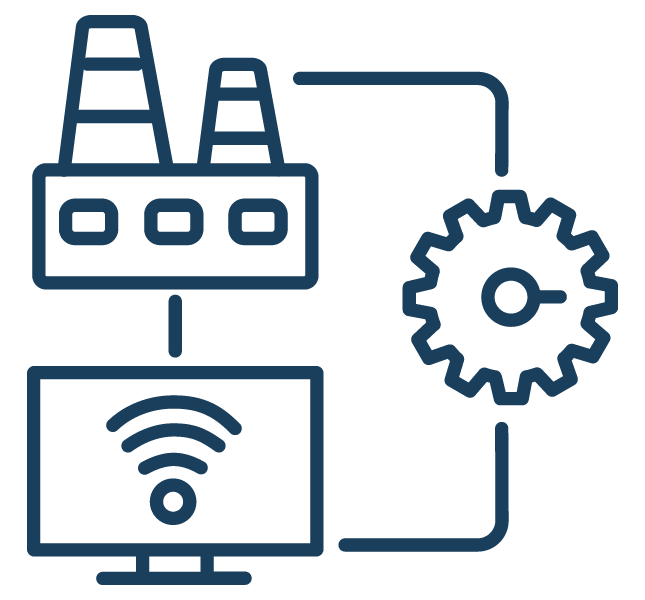
Understanding SCADA
Discover what SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) is and how it works in an industrial setting. This page provides an overview of SCADA, including its components such as computer systems, data connectors, and graphical user interfaces. It explores the importance of SCADA in industries, its ability to monitor and control machinery, and its integration capabilities with other software applications.
Explore the features of SCADA software, including its ability to log data to various databases, provide alarm logging and notifications, connect with different devices and data sources, offer visualization tools, and enable the development of custom automation apps. Learn about the networking features of SCADA that contribute to robust and scalable distributed networking platforms for IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) solutions.
Understand the role of Human-Machine Interface (HMI) in industrial processes and how it functions as an interface between operators and processes. HMIs enable operators to interact with machines without specialized engineering or programming knowledge. They offer information about production rates and equipment status, allowing operators to control and adjust machines and processes. HMIs replace physical wiring and controls, offering programmability and flexibility.
Discover the challenges currently facing HMI systems, such as lack of data input and output, process visualization problems, technology selection complexity, lack of standardization among vendors, and high maintenance costs. Find solutions to these challenges and understand the importance of accessing machinery remotely through HMI systems while addressing potential security concerns.
Learn about the complexities of data analysis and connectivity in IIoT and how SCADA systems can manage and process large datasets efficiently. Discover the significance of competent personnel who can effectively understand and process data to optimize workflow. Consider the benefits of using a mix of technologies in industrial automation, such as improved task differentiation, enhanced usability, cost control, and better customer experience.
Gain insights into the future development of industrial automation with a focus on HMIs. Understand the role of HMIs in monitoring and controlling multiple machines from a single location, enabling efficient operation and interpretation of data. Recognize the wide range of applications for HMI and SCADA systems in various industries, including oil refining, power generation, manufacturing, distributed computing systems, and autonomous vehicles.
In conclusion, HMI and SCADA systems are essential components of the automation process, providing a vital interface between humans and machines in industrial settings.
What is SCADA and How Does it Work?
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. It is a system that is used in an industrial setting to monitor and control machinery. The SCADA system is composed of a computer system which collects data from the machinery, via a data connector or device driver. Also consists of a graphical user interface (GUI/HMI) for monitoring the collected data.
Scada systems today are able to log to open databases, integrate with other software applications like ERP, CMMS, and Analytics programs.
The SCADA system monitors a machine's status and compares it with a predetermined set of values. These values may represent the way the machine is supposed to function, or they may be set by a human operator using input. You can know how efficiently the machine or plant is running by monitoring OEE (Overall Equipment Efficiency).
SCADA systems play a crucial role in industrial automation by providing real-time monitoring and control of machinery and processes. The computer system within a SCADA setup collects data from various sensors and devices connected to the machinery through data connectors or device drivers. This data includes parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and more, depending on the specific application.
The collected data is then transmitted to the graphical user interface (GUI) or human-machine interface (HMI) of the SCADA system. The GUI allows operators and supervisors to visualize the data in the form of charts, graphs, and other visual representations. It provides a comprehensive overview of the machine's performance, status, and operational parameters.
The SCADA system continuously compares the collected data with predefined setpoints or thresholds. These setpoints define the desired operating conditions or limits for the machinery. If the collected data deviates from these setpoints, the SCADA system triggers alarms or notifications, alerting the operators to potential issues or abnormalities. This allows for timely intervention and corrective actions to maintain smooth and efficient operation.
Additionally, SCADA systems offer advanced features like data logging, where the collected data is stored in open databases for historical analysis and reporting. Integration capabilities allow SCADA systems to seamlessly connect with other software applications such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), and analytics programs, enabling comprehensive data analysis and decision-making.
Overall, SCADA systems provide a powerful and centralized control platform for monitoring and managing industrial processes. By leveraging real-time data and intuitive interfaces, SCADA systems empower operators and supervisors to optimize efficiency, detect faults or anomalies, and ensure the smooth operation of machinery and systems.
What are HMI Systems?
HMI stands for Human Machine Interface. It allows humans to interact with machines and other systems.
HMI systems are the next generation of graphical human-machine interfaces that will revolutionize the way we interact with machines. HMIs can be used in any field where there is a need to monitor and control processes, such as manufacturing, medical, aviation, military or industrial facilities.
These systems provide a user-friendly interface that simplifies the operation and control of complex machinery and processes. They utilize graphical elements, touchscreens, buttons, and indicators to enable operators to monitor real-time data, input commands, and receive feedback from the system.
The main purpose of HMI systems is to bridge the gap between humans and machines by providing an intuitive and efficient means of interaction. They allow operators to easily access and interpret information, make adjustments, and respond to system alerts or anomalies.
With the advancements in technology, modern HMI systems offer a range of features and capabilities. They can display real-time data, generate visualizations and reports, offer remote access for monitoring and control, support multi-touch gestures, and even provide voice or gesture recognition for hands-free operation.
HMI systems play a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency, productivity, and safety across various industries. They streamline processes, reduce human error, enable quick decision-making, and facilitate remote monitoring and control. Moreover, HMI systems contribute to better resource utilization, improved quality control, and enhanced overall system performance.
As technology continues to evolve, HMI systems are expected to become more intelligent and integrated with other technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These advancements will further enhance the capabilities of HMI systems and revolutionize the way we interact with machines and systems in the future.
How an HMI Functions as an Interface Between Operators and Processes
An HMI is a software that graphically represents a machine or process. An operator can interact with machines without being an engineer or a programmer. It is an interface between the operator and the process. It can be used in any industry and for any type of process.
It can also provide information about plant assets such as production rates or equipment status.
HMIs allow operators to stop and start machines and processes change parameters, and accomplish lots of other operations that are necessary to change and interact with a control system. Being software, HMI’s can replace physical wiring and controls allowing them to be programmable and flexible.
The HMI (Human Machine Interface) serves as a vital link between operators and processes in various industries. It is a software application that visually represents machines or processes in a graphical format, allowing operators to interact with them without the need for extensive technical knowledge or programming skills.
The primary function of an HMI is to provide a user-friendly interface that enables operators to monitor and control machines or processes effectively. Through the graphical representation, operators can access real-time data, such as production rates, equipment status, temperature, pressure, and other relevant parameters. This information helps operators make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to optimize system performance.
HMIs empower operators to perform various tasks, including starting and stopping machines or processes, adjusting parameters, setting thresholds, and responding to alarms or alerts. The software interface allows for easy navigation and interaction, providing operators with a clear understanding of the system's current state and enabling them to make necessary adjustments as needed.
One significant advantage of HMIs is their flexibility and programmability. Since they are software-based, HMIs can replace traditional physical controls and wiring systems. This programmability allows for customization and adaptation to specific process requirements, making it easier to modify and reconfigure the interface to accommodate changes in the system or process.
Overall, HMIs enhance the efficiency, productivity, and safety of industrial operations by bridging the gap between operators and machines. They simplify complex tasks, improve system visibility, and enable operators to effectively interact with the control system, ultimately leading to optimized performance and better overall control of processes.
Product Features
Best Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Software
An overview of the top SCADA software available in the market. The blog explains what SCADA is and why it is important for industries, followed by a list of the best SCADA software solutions. It also discusses the features, benefits, and pricing of each software to help readers make an informed decision based on their specific needs. Overall, the blog is a useful resource for anyone looking to learn about or purchase SCADA software.
When it comes to choosing the best SCADA software for your industrial needs, it's essential to consider various factors such as functionality, scalability, ease of use, and vendor support. In the blog, we provide an overview of the top SCADA software solutions available in the market. We delve into the importance of SCADA systems for industries and how they can improve operational efficiency.
The blog goes on to present a carefully curated list of the best SCADA software options, highlighting their key features, benefits, and pricing models. This information empowers readers to evaluate and compare different solutions based on their specific requirements and budget.
By providing valuable insights and analysis, the blog acts as a comprehensive resource for individuals and organizations looking to understand SCADA software better and make informed decisions about their automation needs. Whether you're a novice exploring SCADA systems or a seasoned professional seeking to upgrade your existing software, this blog serves as a helpful guide to navigate the SCADA software landscape.
Transforming Industrial Operations with HMI SCADA Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
Highlighting the critical role that HMI SCADA systems play in modern industrial operations, and how they can transform the way processes are monitored and controlled. The comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into the benefits and applications of these systems, as well as their role in enhancing operational efficiency, productivity, and security.
In the comprehensive guide on transforming industrial operations with HMI SCADA systems, we emphasize the pivotal role these systems play in modern industry. By providing valuable insights, the guide highlights how HMI SCADA systems can revolutionize the way processes are monitored and controlled.
The guide delves into the numerous benefits of implementing HMI SCADA systems, ranging from increased operational efficiency and productivity to enhanced security measures. It explores various applications of these systems across different industries, illustrating their versatility and adaptability.
Readers gain a comprehensive understanding of how HMI SCADA systems can streamline operations, optimize resource utilization, minimize downtime, and improve overall safety and compliance. Whether you're a plant manager, process engineer, or technology enthusiast, this guide serves as an indispensable resource to unlock the transformative potential of HMI SCADA systems in industrial settings.
Control Industrial Processes
One benefit of HMI SCADA software is the ability to control and monitor industrial processes locally or remotely.
HMI SCADA software offers the significant advantage of enabling the control and monitoring of industrial processes, both locally and remotely. This feature empowers operators and engineers with the ability to oversee and manage critical operations from a centralized location, regardless of their physical proximity to the machinery.
With HMI SCADA software, operators can remotely start and stop machines, adjust parameters, and execute various operations necessary for interacting with and controlling the industrial processes. This capability enhances operational flexibility, efficiency, and convenience, allowing for real-time decision-making and responsiveness.
Whether it's a single facility or a network of distributed systems, HMI SCADA software provides a robust platform for seamless control and monitoring of industrial processes, ultimately contributing to improved productivity, uptime, and overall operational performance.

Log data in open format to MS SQL Server, Oracle, mySQL, PostgreSQL, InfluxDB, MongoDB, SQLite, MariaDB, Access, SQL Azure, Amazon Aurora, Amazon RDS, Amazon Redshift, Google Firebase, and CSV files
One of the valuable features offered by HMI SCADA software is the capability to log data in an open format to various databases and file formats. This includes popular databases like MS SQL Server, Oracle, mySQL, PostgreSQL, as well as newer options such as InfluxDB, MongoDB, SQLite, MariaDB, and more.
By logging data in open formats, HMI SCADA systems ensure compatibility and interoperability with a wide range of database systems, allowing for efficient data storage and retrieval. Additionally, the software supports storing data in CSV files, providing a flexible and accessible option for data storage and analysis.
The ability to log data in multiple formats enhances data management capabilities, facilitates integration with other software applications, and enables comprehensive data analysis for improved decision-making and process optimization.
Log events to open databases, and send notifications via SMS, email, and voicemail
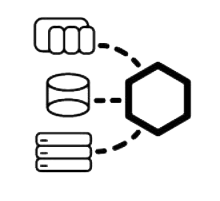
Read and write data to Allen Bradley, Siemens, and Modbus devices, Universal Drivers, OPC, OPC UA, databases, Excel, and read MTConnect.
Build custom Visualizations, User Interfaces, HMIs and Dashboards for Windows, web, as well as native iOS and Android devices
Develop custom automation apps for Windows, web, and mobile devices. Integrate with .NET and REST APIs. Build custom integrated device drivers.

Provides the most robust, scalable, and reliable distributed networking platform for IIoT solutions
Challenges Currently Facing HMI Systems And Solutions
Industrial automation is gaining traction in the market, with the help of HMI. However, there are a number of challenges that are currently facing HMI providers.
These include:
- Lack of data input and output
- Process visualization problems
- Complexity in selecting the right technology
- Lack of standardization among vendors
- Expensive and difficult to maintain

Control & process engineers can now easily and conveniently have access to the machinery they work on. The idea of touchscreen capabilities to control machinery might seem like an unrealistic thought, but it's more than possible. With the massive increase in connected devices, it's becoming a lot easier for engineers to analyze data on the fly and make key decisions from their mobile or laptop.
- The HMI system acts as a bridge between the user and the machine to display information and manage operations. Some of the software also translates data from industrial control systems in to human-readable visual representations. There are many other benefits such outputs and developments will only increase those attributes further. As more and more companies move to the digital, automated space, there are also some related problems that might arise. Here are a few of the most popular ones:
- Remote work seems to be the way for the future with all this amazing new technology. But is it safe? As remote work becomes more popular, there are more ways for a hacker to get into your machine and cause havoc. With distance comes challenges. Expert engineering services are no longer geographical. It makes it possible for businesses to access important information from any part of the world, and also allows them to freely share important KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).
- Data Analysis & Connectivity: One of the tricky things with IIOT is understanding the difficulty in managing all that data. Centralized databases are often used by SCADA systems to maintain control, but they can also be a hindrance when large data sets need to be processed in a timely fashion. This can lead to bottlenecks and delays that could severely hamper operations. When there are these obstacles in place, efficient processing systems need to be established. Empowered Automation Solutions offers a combination of HMI, SCADA and other software that will ensure you have a complete overview of your machinery and the data it produces. This allows for a more efficient operation and interpretation of the data.
- Staffing Issues: As evolving technology changes industrial equipment, the need for personnel who are capable and fluent at using it is also required. This means that it is vital to hire competent individuals who are able to efficiently understand and process data in order to optimize their workflow. The best way to go about it would be to train your employees and make them knowledgeable about working with IoT based on the system.
Using a varied mix of technologies can be difficult at first, but it also has many benefits. People can differentiate the tasks better, machines and operators are more usable and there is a better control of costs incurred. Furthermore, modern technology has enabled the plant to higher flexibility and better customer experience. The touch control panels have also reduced human error which in turn has given the company a competitive edge.
Future Development of Industrial Automation with HMIs in Mind
Industrial automation is the process of using computers and automated equipment to control the operation of industrial machinery in a factory. With an HMI, you can monitor and control multiple machines from a single location.
An HMI is an interface that allows a user to interact with a system or piece of equipment by means other than direct manual operation. The interface may be graphical, as in the case of most modern operating systems, or text-based, as with older mainframe systems.
The future development of industrial automation is closely tied to the continued advancement and integration of HMIs. As technology progresses, HMIs are expected to play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, productivity, and connectivity in industrial settings.
One key aspect of future HMI development is the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies can enable HMIs to analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identify patterns and anomalies, and make intelligent recommendations or decisions. By harnessing the power of AI, HMIs can optimize processes, predict maintenance needs, and detect potential issues before they escalate.
Another area of future development is the incorporation of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in HMIs. AR and VR technologies can provide operators with immersive and interactive experiences, allowing them to visualize and interact with machines and processes in virtual environments. This can facilitate training, troubleshooting, and decision-making processes, reducing the need for physical presence on the shop floor.
Connectivity and interoperability are also essential factors in the future development of HMIs. With the rise of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), HMIs will need to seamlessly integrate with a wide range of devices, sensors, and systems to gather and exchange data. This connectivity will enable real-time monitoring, remote access, and centralized control of multiple machines and processes from a single HMI interface.
Furthermore, advancements in cloud computing and edge computing technologies will enhance the capabilities of HMIs. Cloud-based HMIs can provide access to data and control functionalities from anywhere, facilitating remote operations and enabling collaboration across different locations. On the other hand, edge computing allows for data processing and analysis to be performed closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling faster response times.
In conclusion, the future development of HMIs in industrial automation holds great potential. The integration of AI, AR, VR, enhanced connectivity, and advanced computing technologies will revolutionize the way operators interact with machines and processes. With these advancements, HMIs will become more intuitive, intelligent, and adaptable, driving further improvements in productivity, efficiency, and overall industrial performance.
Conclusion & Closing Remarks about HMI and SCADA
The HMI and SCADA systems are used in a variety of applications for different industries. These systems are used in the control of industrial processes, such as oil refining, power generation, and manufacturing. They are also used to control large-scale distributed computing systems.
They are also used to control autonomous vehicles, such as those for mines, or to control the layout of a warehouse or other industrial facility.
The HMI and SCADA system is one of the most widely used systems in the industry because of its wide range of applications. It is a very important part in the automation process because it provides an interface between humans and machines.