What is Alarm Rationalization?
Types of alarms in SCADA rationalization is an essential practice in industrial process management that aims to ensure a streamlined and effective alarm system. By identifying and reducing unnecessary or redundant alarms, alarm rationalization contributes to the overall safety and efficiency of industrial processes.

Definition and Purpose of Alarm Rationalization
Alarm rationalization refers to the systematic process of evaluating and prioritizing alarms in an industrial environment. Its goal is to identify critical alarms, eliminate nuisance alarms, and ensure that the remaining alarms provide value in terms of safety and operational performance.
The Role of Alarm Rationalization in Industrial Safety
An effective alarm rationalization process is crucial in maintaining operational safety. It helps mitigate the risk of alarm fatigue, where operators may become desensitized to constant, irrelevant alarms, potentially missing critical alerts. By rationalizing alarms, organizations ensure that operators can focus on alarms that are most relevant to the process, improving situational awareness and decision-making.
Identifying Critical Alarms
The first step in alarm rationalization is identifying alarms that are truly critical to process safety. This involves evaluating alarms based on their potential impact on safety, environmental compliance, and operational performance. Critical alarms must be prioritized to ensure timely and appropriate operator response.
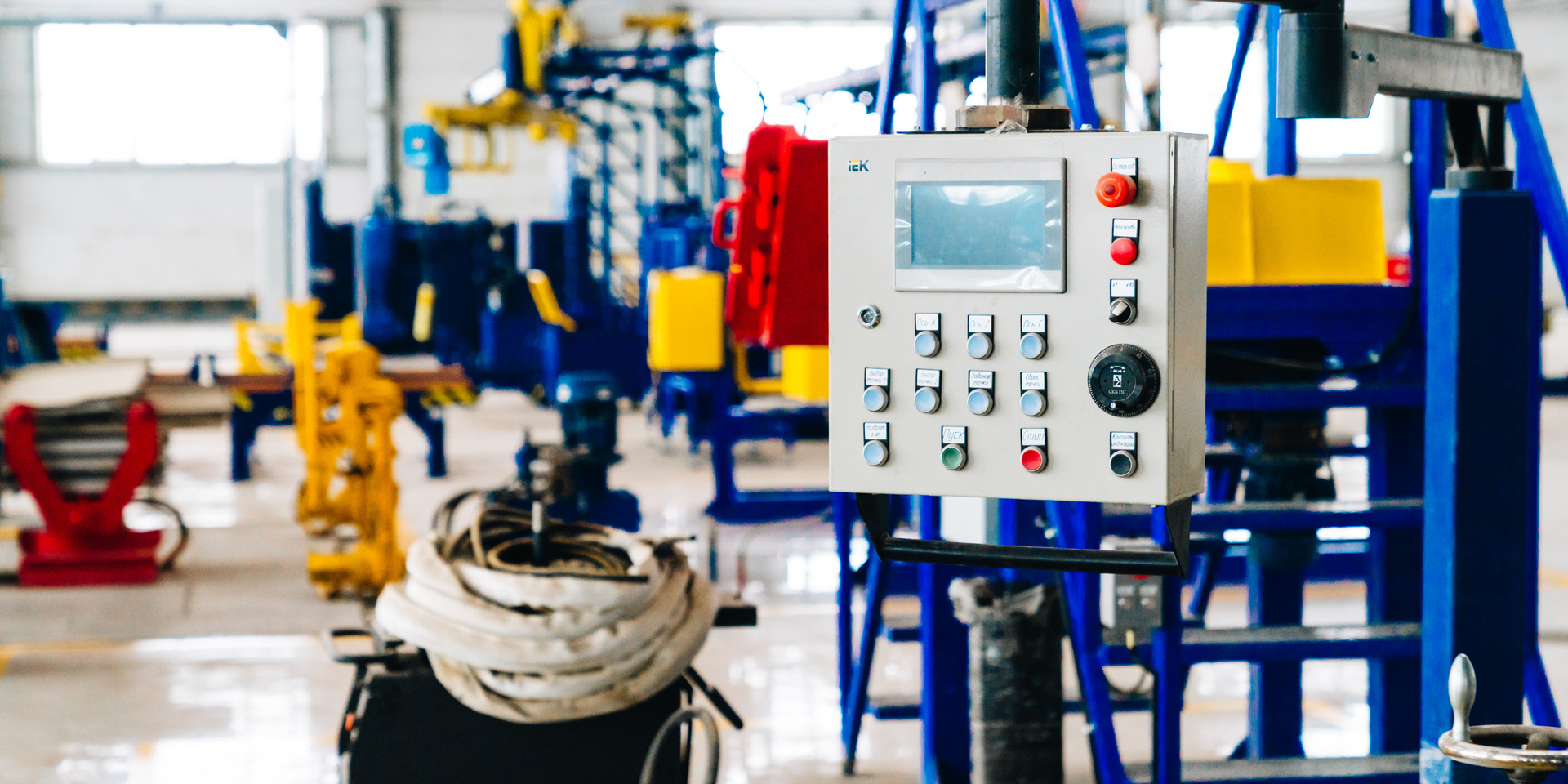

Setting Priorities Among Alarms
Once critical alarms are identified, the next step is to categorize alarms based on their priority. By setting priorities, alarm systems can distinguish between urgent issues and those that can be deferred. This prioritization reduces operator overload and ensures that attention is given to the most pressing issues.
Steps to Effective Alarm Rationalization
Effective alarm rationalization involves a series of structured steps. These steps include:
- Data Collection: Gather data on existing alarms, including alarm frequency, operator responses, and downtime.
- Alarm Evaluation: Assess the relevance and criticality of each alarm based on predefined criteria, such as process safety and operational efficiency.
- System Integration: Integrate rationalized alarms into the alarm management system to ensure proper functionality.
- Operator Feedback: Involve operators in the rationalization process by gathering their feedback on alarm effectiveness and usability.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Alarm rationalization can be complex, with several challenges along the way. Some of the common challenges include:
- Nuisance Alarms: Alarm rationalization helps identify and eliminate nuisance alarms, which do not contribute to safety or efficiency. However, balancing alarm reduction without losing critical data can be challenging.
- Operator Fatigue: Overloading operators with unnecessary alarms can lead to fatigue. Solutions to this problem include better alarm classification and clearer prioritization.
- Changing Operational Conditions: As processes evolve, alarm rationalization must be regularly reviewed to adapt to new conditions. Establishing a continuous review system helps maintain system relevance.
Conclusion
Alarm rationalization is a critical practice for improving the safety, efficiency, and effectiveness of industrial processes. By systematically evaluating and reducing unnecessary alarms, organizations can optimize their alarm management systems, reduce operational downtime, and enhance operator performance. Regular updates to alarm rationalization processes are essential to keep pace with changes in the process environment.
If you're ready to enhance your industrial process safety and operational efficiency, start your alarm rationalization journey today,
contact us!



